The automotive landscape continues to evolve, with constant innovation driving the future of mobility. Two key players in this space, Sonatus, and LHP Engineering Solutions, are excited to announce that, through their strategic partnership, the safety module for Sonatus Automator AI, the Automator Safety Interlock (ASI), is certified by UL Solutions to ISO 26262, achieving ASIL-D capability (automotive safety integrity, Level D). This certification represents the pinnacle of safety assurance in automotive engineering, validating our commitment to delivering cutting-edge, safety-compliant software solutions. ISO 26262, which addresses the functional safety requirements for a vehicle’s electrical and electronics systems, is the global standard for automotive safety. Achieving ASIL-D (the highest safety integrity level) compliance of ISO 26262 provides original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) and their suppliers with confidence that our products meet the industry safety standards required in today’s interconnected vehicle architectures and ensure that the Automator AI platform is fully enabled for safety-critical use cases.
Genesis of a powerful partnership: a conceptual beginning
The partnership between Sonatus and LHP began in early 2023 as a response to a growing challenge: the increasing complexity of software-defined vehicles (SDVs) and their potential safety implications. After developing Sonatus Automator AI, its powerful in-vehicle software orchestration platform, Sonatus recognized the need for functional safety compliance to allow its technology to be used in a broader range of situations in highly interconnected systems, such as those involving safety criticality. As an orchestration framework designed to enhance vehicle quality and driving, Sonatus Automator AI empowers OEMs to create and deploy complex event-triggered workflow recipes, similar to home automation, in which actions are triggered based on certain conditions or events. These recipes allow for introducing new features, executing tests, and performing real-time diagnostic routines on vehicles. The framework supports a flexible range of triggers—including CAN and Ethernet signals, ECU events, and geolocation — facilitating the creation of sophisticated multistage workflows that can be used to target specific vehicles or conditions.
Opening the Automator AI platform up to more participants in the vehicle network greatly enhances possibilities for automation but requires the proper handling of potentially safety-critical use cases. For example, optimizing vehicle dynamics system parameters like torque vectoring or changing the drive mode configuration while the vehicle is moving could pose risks to the driver. Collaboration with LHP proved invaluable in identifying such safety concerns and implementing functional safety mechanisms with customer-specific use case configuration options in mind within ASI. LHP’s industry expertise was crucial to establishing the right assumptions needed to ensure smooth integration of the system with OEMs.
During the functional safety concept phase, Sonatus approached LHP Engineering to begin the process of aligning the platform’s capabilities with automotive safety standards. LHP delivered a comprehensive functional safety evaluation package that included critical safety training for Sonatus managers and engineers and conducted a gap analysis on Sonatus organizational processes to ensure compliance with ISO 26262.
This phase also included essential steps like item definition and hazard and risk assessment (HARA). The key challenge was managing out-of-context development in an evolving ecosystem where software-defined vehicle features are highly dynamic, but safety standards remain static and rigid. These efforts eventually led to the creation of the Sonatus ASI as a guardrail for the vast range of action requests.
Developed as a safety element out of context (SEooC), ASI software acts as a critical operational safety mechanism within the system. ASI independently monitors and validates all action requests as new features are developed and deployed. It verifies that each request aligns with predefined safety conditions and ensures that only authorized and safe operations are permitted. Should an unsafe action be detected, ASI intervenes to guide the system to a predetermined safe state, ensuring vehicle safety is never compromised. See Figure 1.
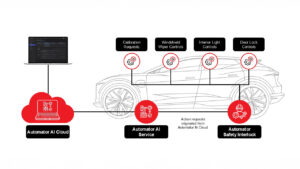
Figure 1. ASI enables the safe configuration of a multitude of controls (only a small subset is visualized here) to enhance automotive solutions, such as vehicle personalization or software-defined components.
Benefits of Sonatus ASI
The ASI software integrates effectively into a POSIX-based system while remaining hardware agnostic. POSIX defines system and user-level application programming interfaces (APIs), along with command line shells and utility interfaces, for software compatibility (portability) with various operating systems. Additionally, the structure of ASI is supported by a complementary safety manual, ensuring comprehensive compliance with automotive safety standards.
The ASI architecture is centered around several critical software functions that collectively ensure reliable operation and adherence to safety standards. See Figure 2.
- Task scheduling and management: ASI incorporates a task scheduling system that ensures tasks are executed in adherence to strict safety timing constraints. This function prioritizes tasks based on their criticality and predefined priority levels and manages process sequences to maintain operational integrity. By coordinating task behavior and timing, the scheduler supports the orderly execution of processes, which is essential for meeting safety requirements and ensuring predictable system responses.
- Start-up validation: To maintain system integrity from the very beginning, ASI includes a start-up test routine that verifies essential parameters and components before the system transitions to full operation.
- State management: ASI incorporates a state machine to manage its operational states, allowing it to respond appropriately to various conditions and external inputs.
- Interface communication management: Effective communication is vital for ASI integration with other vehicle systems. The interface communication manager handles data exchanges, supports adaptable tag-length-value (TLV) message formats, and employs data integrity and validation safety mechanisms. These include cyclic redundancy checks (CRCs), rolling counters, and data validation protocols. These measures ensure that communication errors are detected and mitigated to maintain system safety.
- Action request and approval processes: ASI ensures that only authorized actions and calibration requests are processed. By evaluating incoming action and calibration requests received against predefined criteria, ASI safeguards against unauthorized requests.
- Event and fault monitoring: A fault manager continuously monitors the ASI tasks for anomalies. Detected faults are logged and categorized into different event types and stored in persistent memory, ensuring that event history is preserved. In addition, a snapshot of related data at the moment of an error event is captured and reported. Notifications of fault events, along with their severity levels, are made available to both Automator AI and the vehicle host system, facilitating timely responses and system awareness.
- System diagnostics: Ongoing diagnostics support proactive identification of general process and communication faults.
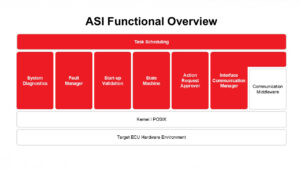
Figure 2. The ASI system architecture (development scope in red) is centered around several critical software functions that collectively ensure reliable operation and adherence to safety standards.
Easy integration
ASI is flexible for integration with different configurations of vehicle host systems and interfaces with other products, such as Sonatus Updater and integrator/OEM-specific solutions. ASI design allows for incorporation into AUTOSAR Adaptive Platform environments, QNX, general Linux OS and real-time Linux systems.
In addition to its software integration capabilities, ASI can be deployed in containerized environments, such as Docker, facilitating shift-left testing and development practices.
Due to its flexible and generic design, ASI can be deployed into a variety of hardware platforms, including high-performance compute and zonal controllers. The modular design of ASI makes it possible to run on the same host as the component it guards or on a separate one, and that separation can be virtual or physical. See Figure 3.

Figure 3. Example configuration: ASI is designed for flexible integration with different vehicle host systems and can interface with other Sonatus products and OEM solutions.
Meeting rigorous safety compliance standards
ISO 26262 compliance requires adherence to stringent requirements at every phase of the development process. Sonatus ASI had to meet approximately 150 specific safety requirements across various stages of development, including architecture design, testing, and analysis. Full traceability allows each requirement to be mapped to specific test cases and safety goals. A particularly noteworthy challenge was managing all the safety specific work products within the safety case, which demands a flawless configuration management system and due diligence by every member of the team.
Conclusion: Innovation meets safety
The collaboration between Sonatus and LHP Engineering Solutions showcases the importance of combining cutting-edge innovation with robust safety systems. By working closely together and engaging early with certification bodies like UL, we created a platform that not only pushes the boundaries of automotive automation but also ensures the highest levels of safety compliance with international standards.
As SDVs continue to reshape the industry, partnerships like this will be key in ensuring that safety remains at the forefront of technological progress.

Figure 4: By engaging early with certification bodies like UL, Sonatus pushes the boundaries of automotive automation and ensures the highest levels of safety compliance with international standards.
There’s a lot more to this topic than is presented here, so check out our announcement about this, as well as additional Sonatus Automator AI resources. We also encourage you to contact Sonatus and schedule a briefing about your company’s unique requirements.
